Key-value (KV) cache is one of the most significant parts of any transformer based LLM model and takes over 30% of the GPU memory during deployment. Hence KV cache plays a critical role in deciding overall LLMs throughput and latency. Recently, various work has been focused on improving KV cache performance either by prompt compression or caching strategies such as cache evacuation and sequence caching.
Now researchers have proposed a novel perspective that is orthogonal to previous efforts: Layer-Condensed KV Cache, a novel method that only computes and caches the KVs of a small number of layers, thus significantly saving memory consumption and improving inference throughput.
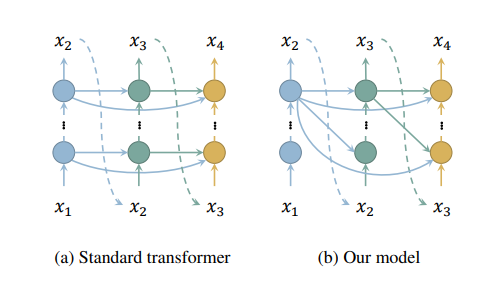
Layer-Condensed KV Cache, a new variant of transformer decoders in which queries of all layers are paired with keys and values of just the top layer so that model do not have to cache or even compute KVs for layers other than the top layer, saving both memory consumption and computation. Furthermore, since models no longer need to compute KVs for these layers, nor do they need to keep the weights WK, WV that map hidden representations to KVs for these layers, thus also saving model parameters.
During experiments on Llama show that this model achieves up to 32× larger batch sizes and up to 26× higher throughput than standard transformers for LLMs of 1B–30B parameters; at the same time, the model has competitive performance to standard transformers in language modeling and downstream tasks. In addition, this method is orthogonal to existing transformer memory-saving techniques, so it is straightforward to integrate them with our model, achieving further improvement in inference efficiency.
Paper : https://lnkd.in/d3XcDA4Z